Technology in AI: How Modern Systems Power LLMs, Security, and Generative Tools
When we talk about technology, the systems and methods used to build, deploy, and secure artificial intelligence applications. Also known as AI infrastructure, it's what makes large language models actually work in the real world—not just in research papers. This isn’t about flashy gadgets. It’s about the hidden layers: how thousands of GPUs talk to each other, how models stay private during use, and why your AI chatbot doesn’t spill your data all over the internet.
Behind every smart AI tool is a stack of core technologies. Large language models, AI systems trained on massive text datasets to understand and generate human-like language. Also known as LLMs, they’re the engine—but they need the right fuel and brakes. That’s where distributed training, the process of splitting AI model training across many machines to handle huge datasets and complex calculations. Also known as multi-GPU training, it’s what lets companies train models faster and cheaper. Without it, you’re stuck waiting weeks for a single model to learn. And when it’s done? AI security, the practices and tools that protect models from tampering, data leaks, and malicious use. Also known as LLM supply chain security, it keeps your AI from becoming a backdoor for hackers. You can’t just drop a model into production and hope for the best. Containers, weights, dependencies—they all need checking. Even the data you feed it has to follow laws like GDPR or PIPL, or you risk fines.
Generative AI doesn’t just write text. It creates images, videos, and even entire UIs—but only if you control the design system. It needs truthfulness checks so it doesn’t lie. It needs retrieval systems so it answers from your own data, not guesswork. And it needs ethical guardrails so teams and users trust it. This collection dives into every layer: how attention mechanisms let models understand context, how encryption-in-use keeps your prompts private, how redaction tools block harmful outputs, and why switching models is sometimes smarter than compressing them. You’ll find real-world benchmarks, deployment traps, and fixes for hallucinations—not theory, but what’s working right now.
Whether you’re deploying a model on-prem, tuning a prompt, or securing a container, the technology behind it all is the same. And if you’re building with PHP, you need to know how these systems talk to your code. Below, you’ll find deep dives into every piece that matters—no fluff, no hype, just the tech that actually moves the needle.
Multilingual Performance of Large Language Models: How Transfer Learning Bridges Language Gaps
Multilingual large language models use transfer learning to understand multiple languages, but performance drops sharply for low-resource languages. Learn why, how new techniques like CSCL are helping, and what it means for global AI equity.
Read MorePrivacy and Security Risks of Distilled Large Language Models - What You Must Know
Distilled LLMs are faster and cheaper but inherit the same privacy risks as their larger models. Learn how model compression creates hidden security flaws - and what you must do to protect your data.
Read MoreScaling for Reasoning: How Thinking Tokens Are Rewriting LLM Performance Rules
Thinking tokens are transforming how LLMs reason by targeting inference-time bottlenecks. Unlike traditional scaling, they boost accuracy on math and logic tasks without retraining - but at a high compute cost.
Read MoreWhy Multimodality Is the Next Big Leap in Generative AI
Multimodal AI combines text, images, audio, and video to understand context like humans do-making generative AI smarter, faster, and more accurate than text-only systems. Here's how it's already changing healthcare, customer service, and marketing.
Read MoreHow to Prevent Sensitive Prompt and System Prompt Leakage in LLMs
System prompt leakage is now a top AI security threat, letting attackers steal hidden instructions from LLMs. Learn how to stop it with proven techniques like output filtering, instruction defense, and external guardrails.
Read MoreMultimodal Generative AI: Models That Understand Text, Images, Video, and Audio
Multimodal generative AI understands text, images, audio, and video together-making it smarter than older AI systems. Learn how models like GPT-4o and Llama 4 work, where they’re used, and why they’re changing industries in 2025.
Read MoreModel Parallelism and Pipeline Parallelism in Large Generative AI Training
Model and pipeline parallelism enable training of massive generative AI models by splitting them across multiple GPUs. Learn how these techniques overcome GPU memory limits and power models like GPT-3 and Claude 2.
Read MoreMulti-Head Attention in Large Language Models: How Parallel Perspectives Power Modern AI
Multi-head attention lets large language models understand language from multiple angles at once, enabling breakthroughs in context, grammar, and meaning. Learn how it works, why it dominates AI, and what's next.
Read MoreConfidential Computing for LLM Inference: How TEEs and Encryption-in-Use Protect AI Models and Data
Confidential computing uses hardware-based Trusted Execution Environments to protect LLM models and user data during inference. Learn how encryption-in-use with TEEs from NVIDIA, Azure, and Red Hat solves the AI privacy paradox for enterprises.
Read MoreError Analysis for Prompts in Generative AI: Diagnosing Failures and Fixes
Error analysis for prompts in generative AI helps diagnose why AI models give wrong answers-and how to fix them. Learn the five-step process, key metrics, and tools that cut hallucinations by up to 60%.
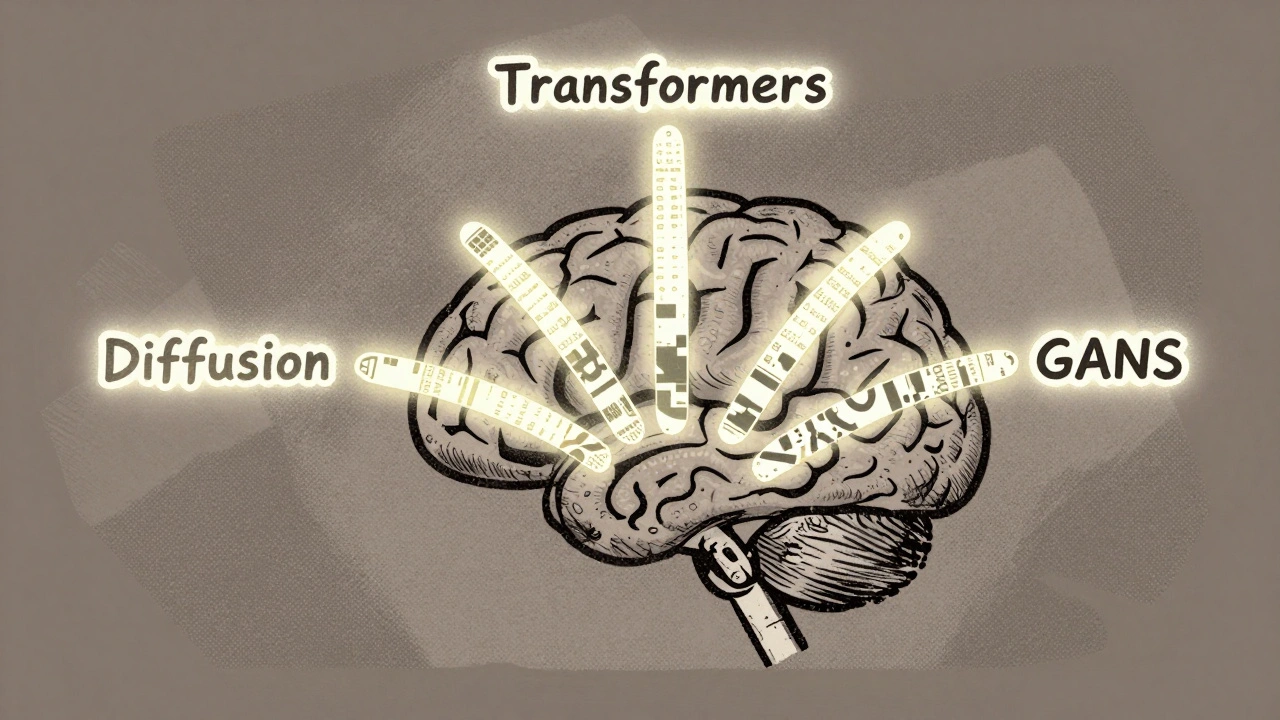
Read MoreFoundational Technologies Behind Generative AI: Transformers, Diffusion Models, and GANs Explained
Transformers, Diffusion Models, and GANs are the three core technologies behind today's generative AI. Learn how each works, where they excel, and which one to use for text, images, or real-time video.
Read MoreHow Generative AI, Blockchain, and Cryptography Are Together Building Trust in Digital Systems
Generative AI, blockchain, and cryptography are merging to create systems that prove AI decisions are trustworthy, private, and unchangeable. This combo is already reducing fraud in healthcare and finance - and it’s just getting started.
Read More